Program Commands
Once a drive has been successfully paired with the robot, it can be used in a robot program. To add a command, switch to the URCaps tab and select Drive. In the right pane, first choose the desired drive and then the command to insert.

Figure: Adding a new drive command to the robot program.
Below is a description of each available command.
Move to Fixed Position
This command moves the drive to a previously saved position. Click Set Position to teach the target position—its value then appears above the Move here button. For testing, click Move here to jog the robot manually to that position. Use Position_Name to assign a descriptive name to the position. With the Wait until position reached and Move simultaneously radio buttons, specify whether the program should wait until the drive reaches the target or immediately continue with the next step.
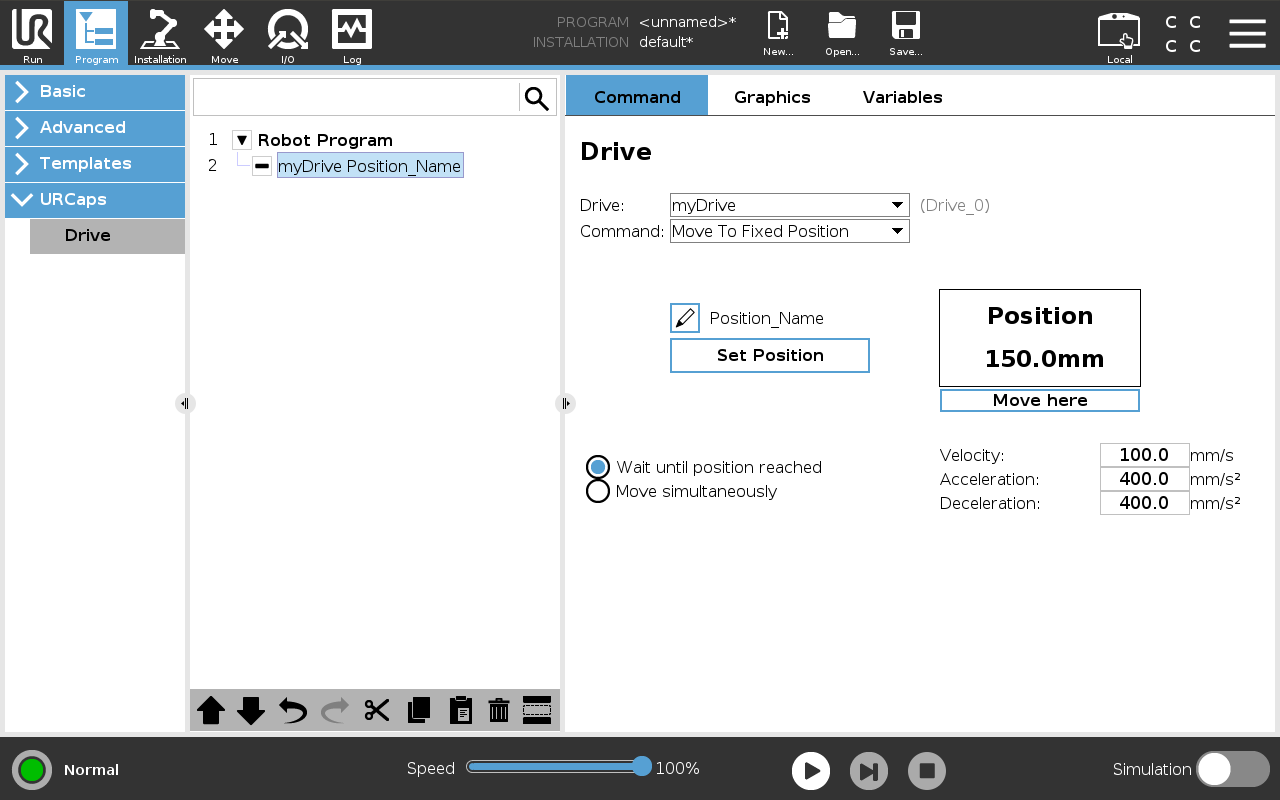
Figure: Command that moves the drive to a fixed position.
Move to Variable Position
This command moves the drive to a target position provided at runtime via a variable. Ensure the variable’s value uses the correct unit—meters for linear axes, degrees for rotary axes. With the Wait until position reached and Move simultaneously options, choose whether to wait for the drive to reach its target or proceed immediately.
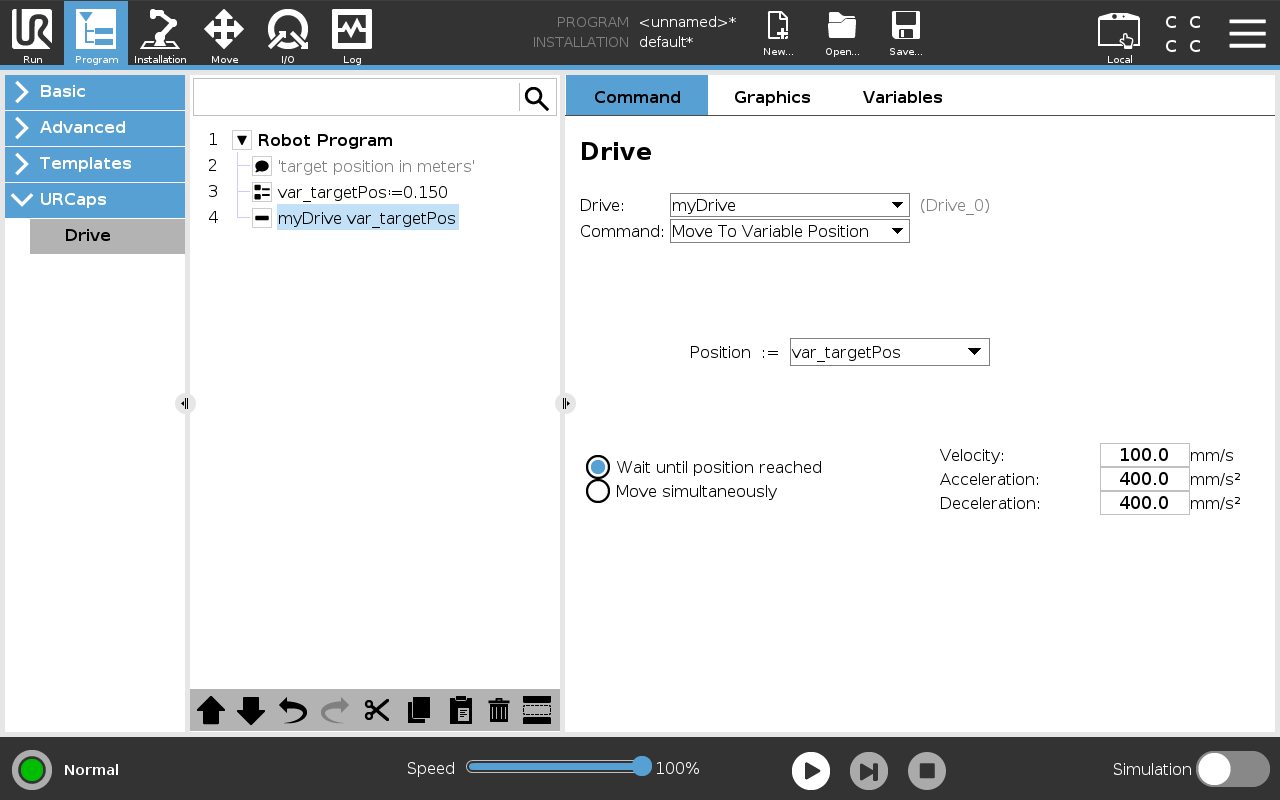
Figure: Command that moves the drive to a variable position.
Move Velocity
This command drives the motor continuously at a given speed in one direction until the Stop Movement command is issued. Use the Positive direction and Negative direction radio buttons to set the direction. Ideal for continuous-motion axes such as conveyors without mechanical end stops.
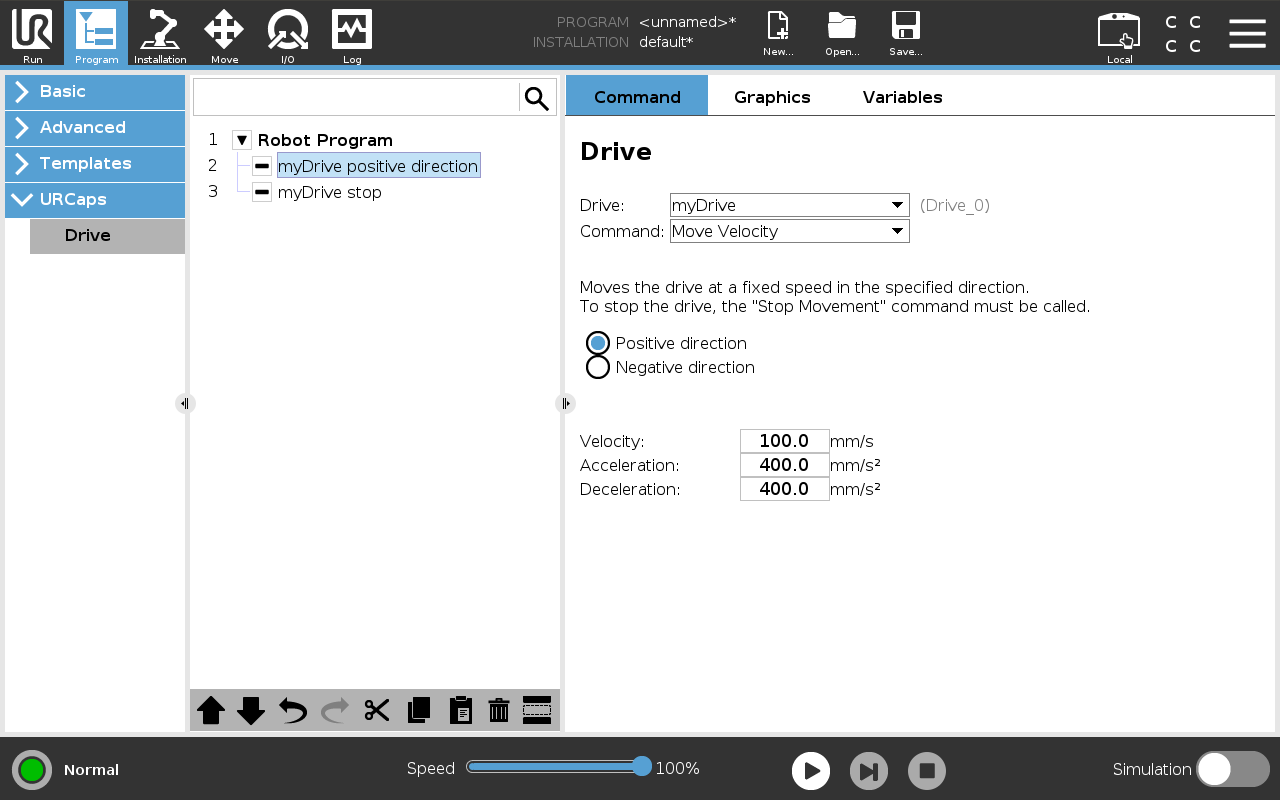
Figure: Command that runs the drive at a constant speed.
Stop Motion
This command stops the drive after it has been set in motion with Move Velocity. With the Wait until drive has stopped and Execute stop simultaneously options, decide whether the program should wait for the drive to come to a full stop or immediately move on to the next command.
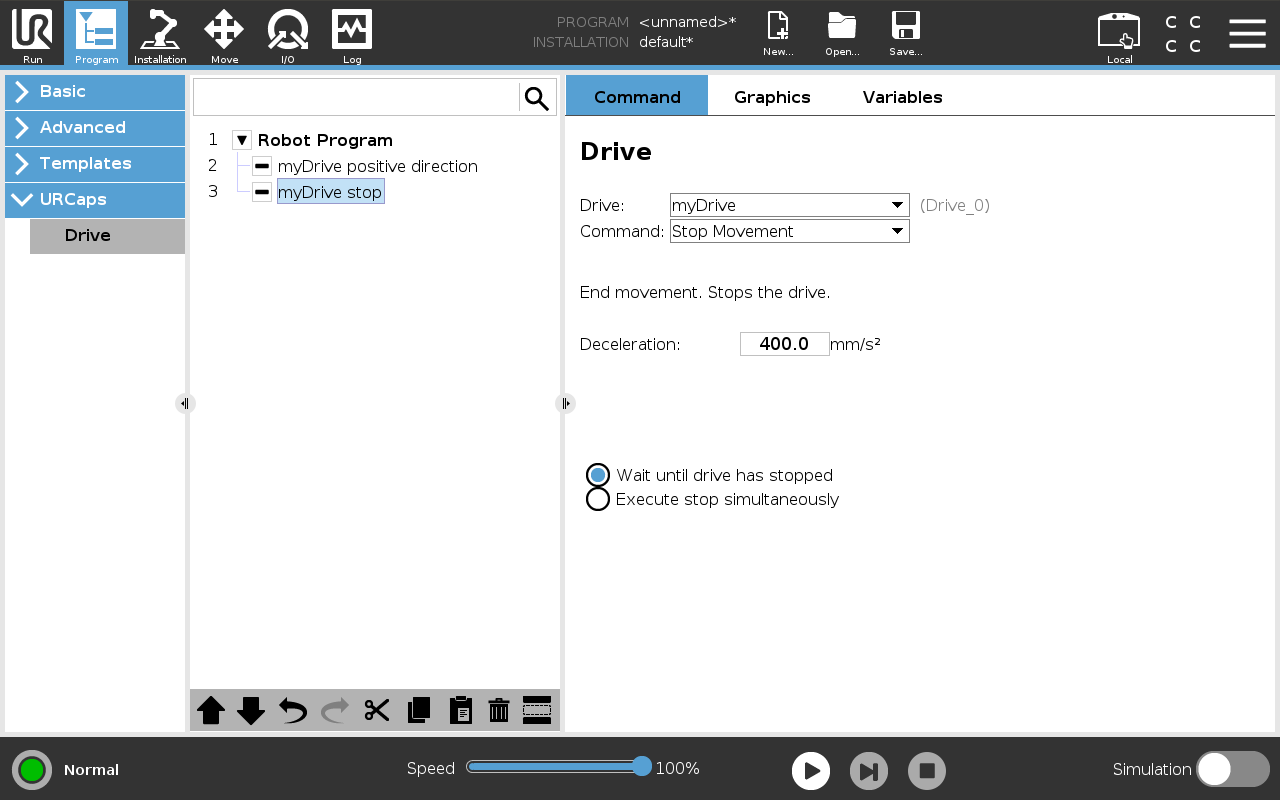
Figure: Command that stops the drive.
Get Position
This command reads the drive’s current position from the controller and writes it into a robot program variable. Note the unit used: meters for linear axes, degrees for rotary axes.
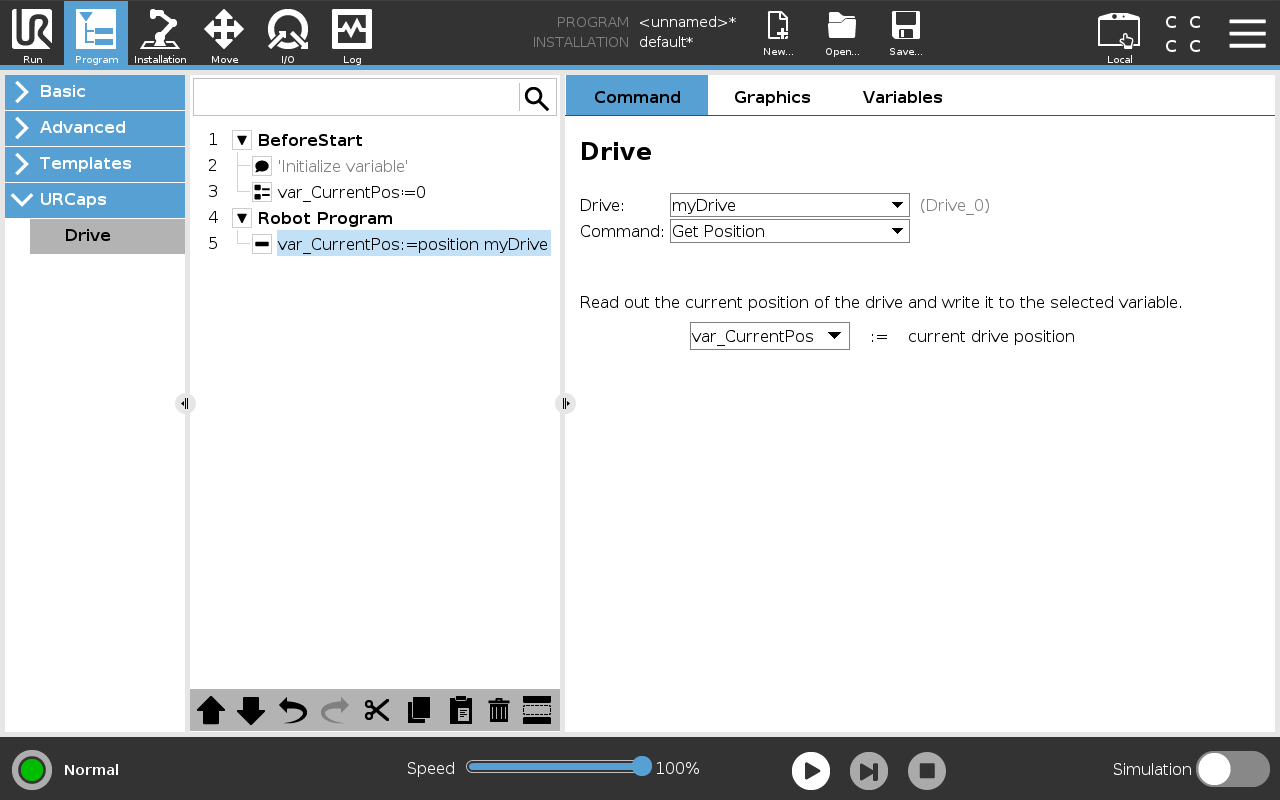
Figure: Command that writes the current drive position to a variable.
Homing
This command performs a homing cycle for the selected drive. Use the always do homing and only when necessary options to specify whether the homing cycle should run every time or only if the drive is not yet referenced. This is especially important for incremental encoders, which must be rehomed after each power loss. Placing the homing command appropriately in the program prevents collisions during the homing.
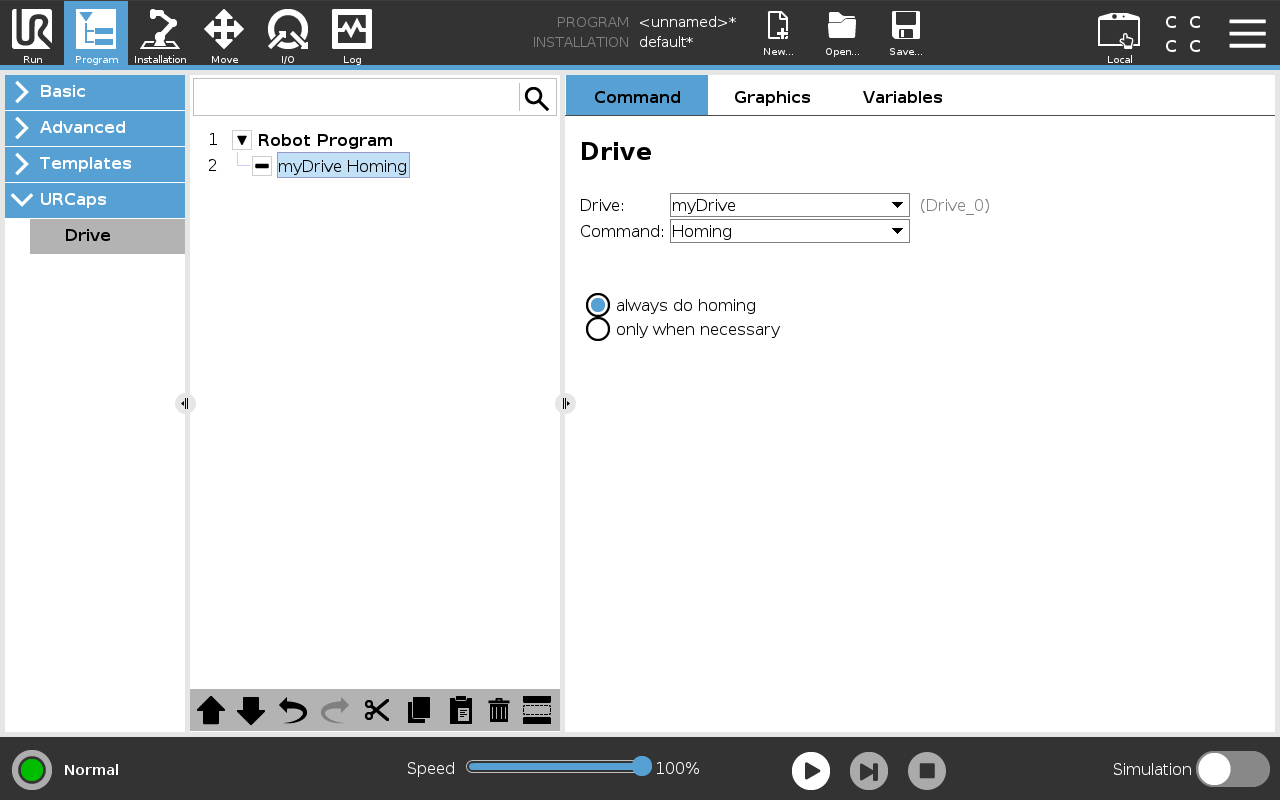
Figure: Command that executes a homing (reference) cycle for a drive.